Employee Retention and Workforce Reengineering
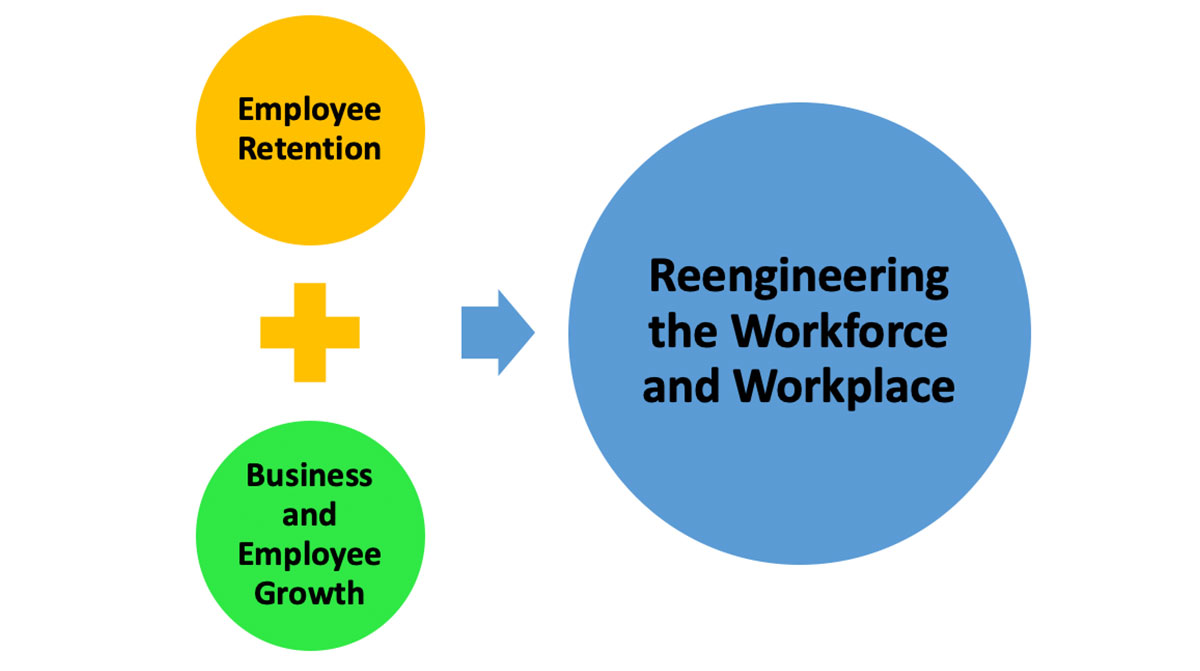
As small and medium size business emerge from the pandemic, they are encountering two significant and interacting challenges: the retention of valued employees to the business and the redeployment of human resources to support the growth of the business and at the same time accommodate the needs of its employees.
These emerging forces are converging to compel corporate leadership to consider measured approaches to reengineering their workforce.
The retention of valued contributors to the success of the business is becoming a major challenge throughout all industries. The loss of experienced employees to competitors, or allied industries, is approaching epidemic proportions and thus becoming more critical as companies are finding it increasingly difficult to replace them.
Informed corporate leaders are carefully considering strategies to address the factors that contribute to employees leaving the company for greener pastures.
The days of simply relying on HR recruiting methods to hire required numbers of qualified employees from an abundant talent pool is over for the foreseeable future.
The present concurrent staffing focus is on retention tactics working in correlation with recruiting approaches to maintain an effective workforce for the future. Linked to implementing effective staff preservation and recruitment strategies is the reengineering of a flexible and agile workforce deployment strategy.
This article offers [1] an examination of the factors that contribute to employee flight, [2] best HR employee retention practices, and [3] reengineering strategies that go beyond restructuring and rearranges the boxes on the organization chart.
It is extremely important for the company to ensure they have the proper Human Resources expertise and leadership that can develop, drive and execute plans and procedures in order to sustain a thriving workplace. Organizations are turning to HR firms like Flex HR to support their capacity-development needs.
Causes of Employee Turnover
The factors contributing to staff turnover are varied and often complex. But there is rarely just one cause for an employee to leave the company. Here are some of the primary contributors to staff turnover:
- Lack of Career Growth and Progression: If employees perceive that they are in a dead-end job with no opportunities to grow within the company the risk of turnover is high. This is especially true among millennial employees.
- Company Failure to Stay Current: If the company does not incorporate new technologies or innovative approaches to the business, employees will look to other organizations that embrace change.
- Ineffective Management Practices: Incompetent managers who fail to recognize employee contributions to the business, cannot manage differences well, employ corrosive management tactics, and fail to grow the capabilities of the staff, will contribute to employee turnover.
- Compensation Shortfalls: If a business does not provide competitive salaries, particularly in industry-related positions, the risk of losing the employee to a competitor is high. The corollary then also becomes a risk factor, namely, relying on compensation only as a means of buying the loyalty of the employee.
- Lack of Social Engagement: Recent experiences occasioned by the pandemic, and the associated work-from-home experiments, have highlighted the need for employees to engage socially with their co-workers in conducting their job responsibilities. The notion that all employees prefer to work at home has subsided.
- Failure to Promote Diversity: The workforce in every industry is becoming more diverse. Companies that fail to make a commitment to diversity, which is a primary component of their culture, will alienate sectors of their workforce and contribute to staff turnover.
- Change of Circumstance Conditions: A spouse relocation, the birth of a child, a serious illness of a relative, among other life changing circumstances all contributes to staff turnover. While the company has little control over these situations, the response of management to these employee circumstances is observed closely by fellow employees.
- Management of Change: As the company considers restructuring, redeployment of employees and changes in employee job responsibilities and reporting relationships, failure to adequately communicate, support, and effectively promote employee ownership of the change will provide a turnover risk for the company.
Employee Retention Best Practices
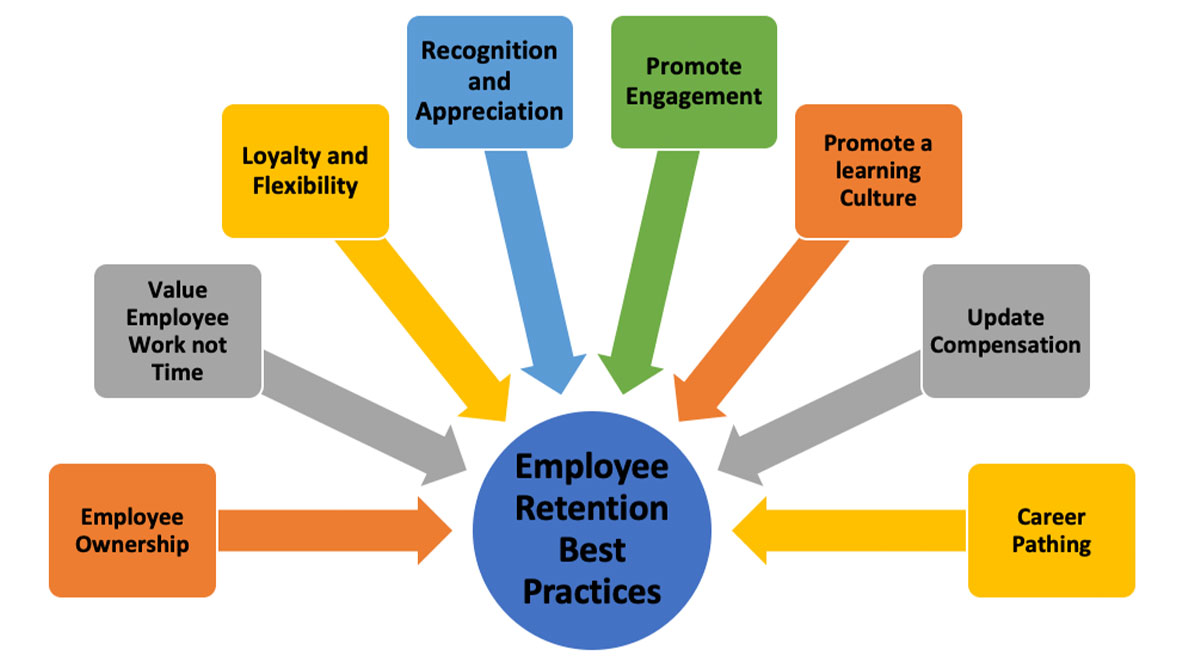
When considering employee retention best practices, corporate leaders should always calibrate retention plans to the business goals of the company. It is the job of Human Resources to outline the requirements for preserving valued employees, which should shape the changing competency and capacity needs of the company year over year. Workforce retention is not necessarily an objective; however, it’s a major key player to the business goals as a whole in order for the company to evolve.
The components of an effective retention strategy and program are presented in the following diagram.
The implementation of retention techniques is the responsibility of management, with the help of HR and executive leadership. The first line of supervision begins with orientation and continues throughout the employee’s tenure with the company.
The following standards and criteria to retention best practices that shape the culture of the organization include:
- Promote employee ownership of their work by encouraging insights on how their work efforts and their performance can be improved.
- Place value on employee accomplishments, not on the time they devote to the work assigned to them.
- Employee loyalty to the company is directly related to the degree of flexibility given to the employee to balance work obligations with personal obligations.
- Recognize work well done by the employee by making their work outcomes and results explicit in support to corporate objectives.
- Promote collaborative engagement between employees in solving unit, department and company problems and challenges.
- Facilitate a culture of learning where error is seen as a learning opportunity to advance performance and not a reason to punish or devalue the employee.
- Update compensation structure review on a regular basis to ensure compatibility with industry standards.
- Institute a career progression system tied to measurable performance management objectives and metric criteria communicated to the employee before an established review period. Consider succession planning for targeted executive leadership positions.
Employee Retention System Model
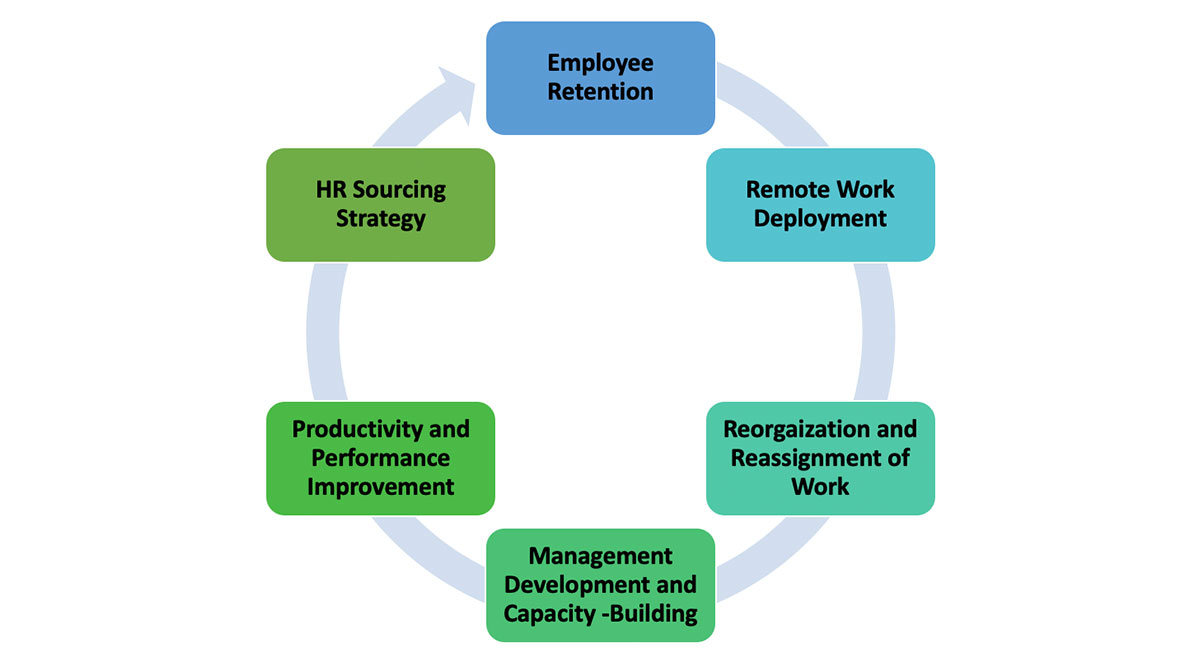
Employee retention procedures taken together with sound management practices drive the planning and executing of reengineering initiatives including HR sourcing strategies, deployment of remote work systems and policies, reorganization and reassignment of work, management of change, management development and employee capacity-building, as well as productivity and performance improvement.
The employee retention system model below shows the interconnection and relationship between retaining employees and the actions organization can take to maintain and enhance employee retention.
Consequently, these properly administered actions serve not only as the basis for achieving value-added employee job satisfaction, motivation, and higher levels of productivity but also reenforces the employee’s commitment to the company and promotes employee retention. Flex HR consultants are prepared to guide organizations to effectively deploy these actions to achieve higher retention levels of valued employees.
Contact us now to get the solutions to maximize your HR needs today!